Buy cheap, buy twice. Some small businesses and freelancers hire the cheapest agency or freelancer and end up having to create their website all over again. Web development is a complicated process that involves marketing, design, search engine optimization, design, and copywriting. Websites need to have:
- readable typographic design,
- organized information architecture,
- an optimized search engine structure complete with contents to reach the right target,
- marketing and copywriting to communicate right target and convert them to paying customers.
Web Content Translation is the same. Translated texts should be search engine optimized to communicate the right target into buying your products or to contact you for a price quote. Care must be taken to not violate any laws, like the Act Against Unjustifiable Premiums and Misleading Representation (景品表示法)((Japanese Law Translation – [Law text] – Act Against Unjustifiable Premiums and Misleading Representations)), that prohibits expressions like “the best” or “effective” without supporting evidence. Some copy may not work in target countries because of social and economic environments, like local competitors or the local business platform. However, it is highly unlikely to find specialists in all three fields (marketing, law, and copywriting) for a reasonable price.
It does not take someone with a bar certification or 40 years experience in copywriting to translate web content. So what is the essential level of marketing, copywriting, design, and legal skills for English to Japanese translators and how can you find out if your translators have them?
Translators need to know Marketing
In Norway, a Big Mac costs $5.65 USD and the GDP per person is $97,013 USD, which means on average Norwegians can buy 17,170 Big Macs a year. This makes Big Macs casual food for the average Joe in Norway. In India, a Big Mac costs $1.83 USD and the GDP per person there is $1,627 USD which means on average Indians can buy 889 Big Macs a year. This means a Big Mac is fancy food for rich people and tourists in India. (Interactive currency-comparison tool: The Big Mac index | The Economist)
Marketing is not as simple as that, but this “Big Mac Index” demonstrates that when entering an overseas market, you need to consider changing price and/or adjust your marketing approach due to different pricing and economic environments.
The above information should be collected and considered before entering an overseas market and translating websites, posters, product catalogs, or anything related to marketing. However, overseas market research is not only time consuming but also difficult to execute because of language barriers. In many cases, it is more efficient to go ahead and translate marketing materials.
Translators would not know when price of product is a “super deal” or “cheaper than everyday milk” and they should report to the project manager when the text doesn’t fit the local market. Marketing is not only about pricing. There might be a local competitor that conflicts with the Unique Sales Proposition of your products. There might be a local distribution channel or another platform for selling. Translators have no language barrier to make local marketing research harder. They should know the target audience and possess the customer insight to write sales copy. Who better than translators to conduct local market research?
Translators need to know laws
In the U.K., “low in alcohol” is defined between 0.5% and 1.2% alcohol by law and advertisers cannot claim the drink is “low in alcohol” if it contains more than that.
Regulation of advertisements is different in each country. You might be tempted to ignore the laws, but the cost of losing your customers’ trust is greater than any fine. Regulations in Japan are very strict compared to most western countries.
Act Against Unjustifiable Premiums and Misleading Representations (景品表示法)
The Act Against Unjustifiable Premiums and Misleading Representations is a part of the Japan Anti-Monopoly Law, which regulates deceptive consumer practices. The law prohibits representation on the quality, quantity, standards, or likes from being shown much better than reality or representation without evidence that supports the claim. For example, the law prohibits phrases like “the best” or “effective” without supporting evidence. The law also prohibits false discounts that misleads consumers about the regular price, discounts, and several other things.
Regulation for specific products
There are also specific requirements that apply to certain sectors, such as:
- Food, supplements, and medicines (Pharmaceutical Affairs Law (Japan) – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia) (日本法令外国語訳データベースシステム – [法令本文表示] – 食品衛生法)
- alcohol
- beauty products
- environmentally-friendly products
- tobacco
For example, most supplements are categorized to “food” because of lack of evidence to prove the effect of the supplement.
Specified Commercial Transaction Law (特定商取引法) (Japanese Law Translation – [Law text] – Act on Specified Commercial Transactions)
Specified Commercial Transaction Law regulates types of transactions, including door-to-door sales, mail-order sales, and online shops. All online shops are legally mandated to place “特定商取引法に基づく表示”, which means “display based on specific trade law” that includes price, payment method, name of company, address of company, phone number, name of company representative, etc. Although the law does not apply to foreign entities that sells products or services to Japanese, having this would help businesses gain trust from customers.
Translators need to know SEO
You might be walking through a small, quiet street when you stumble upon a nice, hidden cafe with unmarked entrances. That never happens on the internet because you need to enter specific keywords and click “next” many times to find hidden websites. Websites need to be optimized to be found by the right visitors. The technique to achieve that is called Search Engine Optimization (SEO).
One of the most important components of SEO is keyword optimization: use keywords that users search on key components of website including title, meta-description, header tags, alt keywords of images, category, etc. When translating websites, translators need to use keywords with high volume in natural text.
Search Engine Optimized translation improves ranking on Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs), drives traffic, and increases awareness in search engines. Making translated texts search engine friendly takes very little effort, but the impact of it, or rather the impact from the lack of it, is not so small. You want to make sure that translators have established an efficient process to deliver SEO translation.
Translators need to know copywriting
Copywriting: many may think they know what it is, but few know what it really is. The difference between writing and copywriting is that writing is usually to inform whereas copywriting is to get people to take action.
The word “copywriter” includes the word “writer”, but copywriters spend often very little time writing in copywriting process.
Copywriting projects consist of:
- research and analysis of marketing environments, including customer insight and competitors,
- an interview with a product planning manager,
- editing,
- proofreading,
- sourcing and editing images, and
- planning and implementing marketing campaigns.
Copywriting projects are often executed by a team consisting of a creative director, market researchers, graphic or video editors, and copywriters.
Copywriting, since copywriting is a part of marketing and marketing is a part of copywriting, requires adjustments to local market environments when entering foreign markets. However, executing the entire copywriting process, including marketing research and graphic design is not only an expensive option, but also runs the risk of creating a different brand image in the foreign market.
An affordable solution to localize websites is to hire a native translator with marketing and copywriting experience for all important components of copywriting: market research, writing and design.
Translators need to know design
Localization necessitates the rethinking of even visual design. Let’s take a look at a big international company with successful localization. The Coca-Cola Company has different eye-catching images and designs for 20 different locations.
However, design localization is not only an expensive option, but may also compromise brand identity. Having an internationally unified design has its advantages, including coherent branding, efficiency, lower cost, and less complication.
So what design components can be localized without compromising brand identity?
Eye-catching images
Which photo is a better eye-catching image for a web page about affordable family health insurance for middle class Japanese in Japan? It does not take a fancy survey or an academic paper to tell that the Japanese audience can relate to the picture on the left more. It takes very little effort or cost to replace and localize photos. There are many stock photo websites that you can download stock photos available for commercial projects for free or for very little money.

Color-palettes
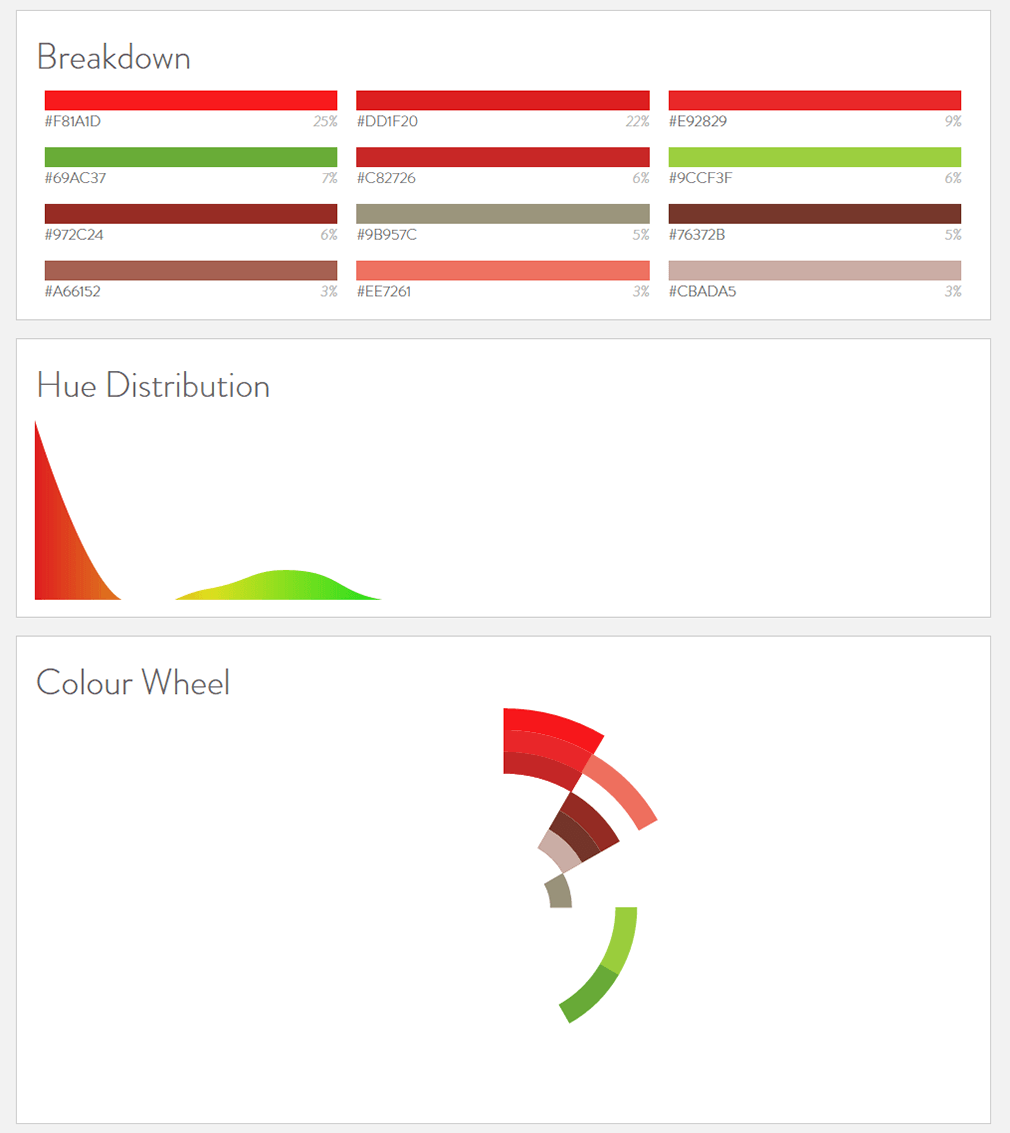
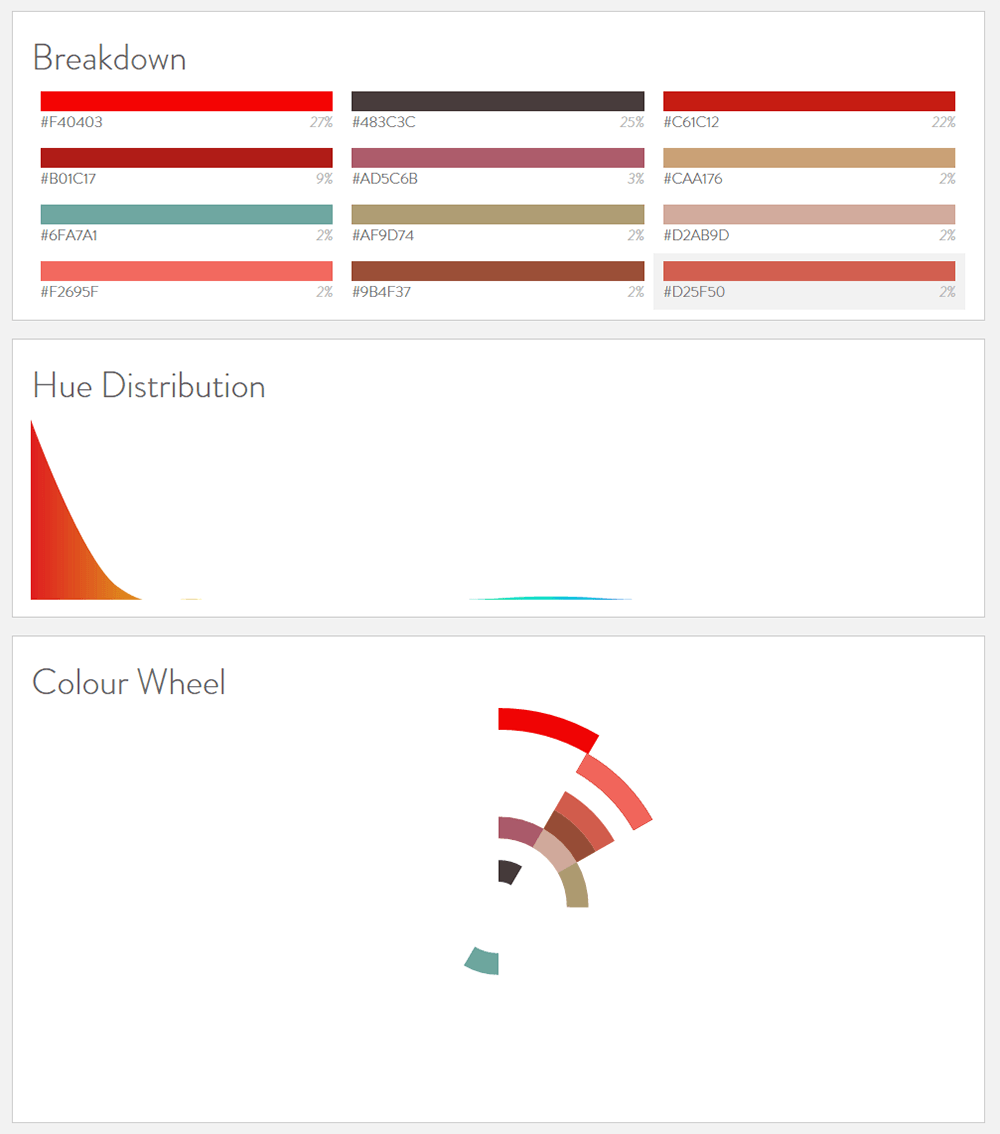
The Coca-Cola page has different color palettes. Except for the Coca-Cola trademark red “F40009”, each red and green color has slightly different saturation. For example, the saturation of green on the post header is darker on the Japanese website.

Typography

This is what many people think of when they hear the word “typography”, but typography isn’t just a creative graphic design. It’s also setting the right kerning, line-height, typeface, color, and size to assure readability, legibility, visibility, as well as delivering your brand message. This is reason why designers spend days and weeks to create a logo with original typeface that represents a company’s brand identity. This is why The New York Times, both newspaper and website, are beautiful even though they have very few colors and graphics.
Typography is equally in important in Japanese (see more at Guide to Web Typography in Japanese) or in any other language. Arabic, for example, is a right-to-left writing system, so left-to-right web design is almost disturbing to users. Traditional Chinese and Japanese have very complicated logo-graphic characters called Kanji (漢字). Whereas the highest stroke count of the English alphabet is 4, the highest stroke of Kanji is 84. The highest stroke Kanji that college students should be able to read and write is 23, “艦”. The highest stroke Kanji that is included in font-file, MS Gothic or MS Mincho, is “麤”, 33 strokes. Obviously, you should never use less than a 12-pixel font.
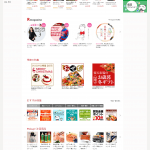
Rakuten ichiba, is the biggest online shop in Japan, even bigger than Amazon. (Total e-commerce distribution in Japan in 2012 is 1 trillion 450 billion yen. Rakuten market share is 28.8% and Amazon market share is 12.4% according to Amazonの日本売上高が判明 12年は78億ドル – ITmedia ニュース and 楽天、売上高・営業利益が過去最高に – ITmedia ニュース). Rakuten Ichiba is trying to develop their overseas market, and yet not many westerners have even heard its name. One of the likely reasons for this is because the design has been completely optimized to the Japanese audience. It’s so optimized, in fact, that it is already not user-friendly to non-Japanese users. Open Rakuten Ichiba and translate the website using Google Translate. I am sure you will be surprised.
Localization allows companies to expand their market overseas. If the product is right, the market can be your blue ocean where there are plenty of customers and very few competitors. However, that’s only when localization is properly done.





[…] 5 overlooked elements of Web Content Translation that makes successful localization […]